Immediate Life Support (ILS) is a vital resource for healthcare professionals and first responders, providing essential knowledge to manage critical situations and save lives effectively․
1․1 Definition and Importance of ILS
Immediate Life Support (ILS) is a systematic approach to assessing and managing critically ill patients, focusing on airway, breathing, circulation, and disability․ It emphasizes early recognition and intervention to prevent deterioration․ ILS is crucial for healthcare professionals, including nurses, paramedics, and medical students, as it provides the skills to stabilize patients during emergencies․
The importance of ILS lies in its ability to improve patient outcomes by addressing life-threatening conditions promptly․ It equips responders with the knowledge to manage cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, and other critical situations effectively․ Free downloadable manuals and guides are widely available, making ILS training accessible for all healthcare providers, ensuring they can deliver high-quality care in emergencies․
1․2 Target Audience for the Manual
The Immediate Life Support (ILS) manual is designed for healthcare professionals, first responders, and medical students who require the skills to manage critically ill patients․ It is particularly beneficial for paramedics, nurses, and dental workers, as well as those preparing for exams like the ORE examination․ The manual serves as a valuable resource for anyone involved in emergency care, providing practical guidance on assessing and treating patients effectively․
By offering free downloads, the ILS manual ensures accessibility for a wide range of practitioners․ Its content is tailored to enhance the abilities of healthcare providers, enabling them to deliver high-quality care during critical situations․ Whether for training or reference, the manual supports continuous learning and skill development in life-saving interventions․
Key Components of the Immediate Life Support Manual
The manual covers essential areas for effective emergency care, including patient assessment, airway management, breathing, circulation, and exposure considerations․ It serves as a practical guide for healthcare professionals․
By focusing on critical life-saving techniques and protocols, the ILS manual ensures comprehensive training and preparedness for medical emergencies, making it a valuable resource for free download and reference․
2․1 The ABCDE Approach to Patient Assessment
The ABCDE approach is a systematic method for assessing patients in life-threatening situations, focusing on Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure․ This structured process ensures that healthcare providers prioritize critical areas first, starting with maintaining a patent airway and adequate breathing, followed by assessing circulation and neurological function․ Exposure is essential for identifying potential injuries or conditions that may require immediate attention․ The Immediate Life Support Manual emphasizes this approach as a cornerstone of effective patient care, providing clear guidance on each step․ By following the ABCDE framework, professionals can quickly identify and address life-threatening conditions, improving patient outcomes significantly․ This method is widely taught in ILS training programs and is accessible through the free downloadable manual, making it a vital resource for all healthcare workers․
2․2 Airway Management Techniques
Airway management is a critical component of immediate life support, focusing on ensuring a patient’s airway is clear and functional․ Techniques include airway positioning, such as the head-tilt chin-lift maneuver, and the use of airway adjuncts like oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways․ Suctioning is also essential to remove obstructions such as vomit, blood, or fluids․ The manual emphasizes the importance of recognizing when advanced airway management, like endotracheal intubation, is necessary․ Proper training and practice are vital to master these skills․ The Immediate Life Support Manual provides detailed guidance on airway management, including step-by-step instructions and practical examples, making it an invaluable resource for healthcare professionals․ This section ensures that providers can effectively manage airways in emergencies, improving patient outcomes significantly․
2․3 Breathing and Ventilation Strategies
Breathing and ventilation strategies are vital for maintaining adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal in critically ill patients․ The manual outlines techniques such as bag-valve-mask (BVM) ventilation and the use of mechanical ventilators․ Proper ventilation rates and tidal volumes are emphasized to avoid lung injury․ Oxygen therapy is discussed, including the appropriate use of nasal cannulas, face masks, and high-flow devices․ The importance of synchronizing ventilation with the patient’s respiratory efforts is highlighted, especially in cases of respiratory distress․ The Immediate Life Support Manual also covers troubleshooting common ventilation issues, such as inadequate chest rise or high airway pressures․ These strategies ensure healthcare providers can effectively support patients’ breathing needs during emergencies, improving outcomes and preventing complications․
2;4 Circulation and Cardiac Arrest Management
Circulation and cardiac arrest management are critical components of immediate life support․ The manual emphasizes the importance of maintaining adequate blood flow to vital organs, particularly during cardiac arrest․ Techniques for assessing circulation, such as checking pulse and capillary refill, are detailed․ Management strategies include hemorrhage control, fluid administration, and the use of vasopressors․ Cardiac arrest protocols are outlined, focusing on high-quality CPR, including chest compression depth and rate․ The role of defibrillators in restoring a viable cardiac rhythm is also highlighted․ The manual stresses the need for timely intervention to prevent organ failure and improve survival rates․ These strategies are essential for healthcare providers to manage cardiac arrest effectively and ensure the best possible patient outcomes․
2․5 Disability and Exposure Considerations
Disability and exposure are crucial steps in the immediate life support process․ Assessing neurological status helps identify potential brain injuries or impairments․ The AVPU scale (Alert, responds to Voice, responds to Pain, Unresponsive) is commonly used․ Exposure involves carefully examining the patient to identify hidden injuries or conditions․ This includes removing clothing to check for wounds, bruises, or signs of bleeding․ Proper exposure ensures comprehensive assessment and timely intervention․ Maintaining patient dignity and comfort is essential during this process․ These steps are vital for prioritizing care and preventing overlooked complications․ They complement the ABCDE approach, ensuring a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition․

Cardiac Arrest and Resuscitation
Cardiac arrest requires immediate intervention to restore heart function․ Effective CPR and defibrillator use are critical for improving survival rates and neurological outcomes․ Prompt action is essential․
3․1 Recognizing Cardiac Arrest Symptoms
Recognizing cardiac arrest symptoms promptly is crucial for effective intervention․ Common signs include sudden collapse, loss of consciousness, and unresponsiveness; The patient may stop breathing or exhibit abnormal breathing patterns, such as gasping․ A lack of pulse, particularly in the carotid artery, is a key indicator․ Additionally, pale or blue-tinged skin and seizures may occur․ It is essential to act quickly, as delays can worsen outcomes․ High-risk individuals, such as those with chest pain or severe shortness of breath, should be closely monitored․ Bystanders and healthcare providers must remain vigilant to these signs and initiate CPR immediately if cardiac arrest is suspected․ Early recognition saves lives and improves recovery chances․

3․2 CPR Techniques and Best Practices
Proper CPR techniques are essential for maintaining blood circulation and oxygen delivery during cardiac arrest․ Begin with chest compressions, placing hands on the center of the chest, one on top of the other․ Compress to a depth of 2-3 inches at a rate of 100-120 per minute․ For trained responders, provide rescue breaths after every 30 compressions․ Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available, following its voice prompts․ Ensure minimal interruptions to chest compressions and rotate rescuers every 2 minutes to prevent fatigue․ Maintain a ratio of 30:2 for compressions-to-breaths if two rescuers are present․ Continuous, high-quality CPR improves survival chances and neurological outcomes․ Always follow local protocols and update training regularly to refine skills․
3․3 Defibrillator Use and Protocols
The use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) is critical in cardiac arrest situations to restore a normal heart rhythm․ Turn on the device, attach pads to the patient’s bare chest as instructed, and follow voice prompts․ Analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if advised․ Ensure no one touches the patient during shock delivery․ After the shock, resume CPR immediately․ Repeat the cycle as directed by the AED; Training is essential to understand proper pad placement, device operation, and safety protocols․ Always follow local guidelines and manufacturer instructions․ Regular updates to protocols ensure compliance with the latest resuscitation standards․ Timely defibrillation significantly improves survival rates in cardiac arrest scenarios․
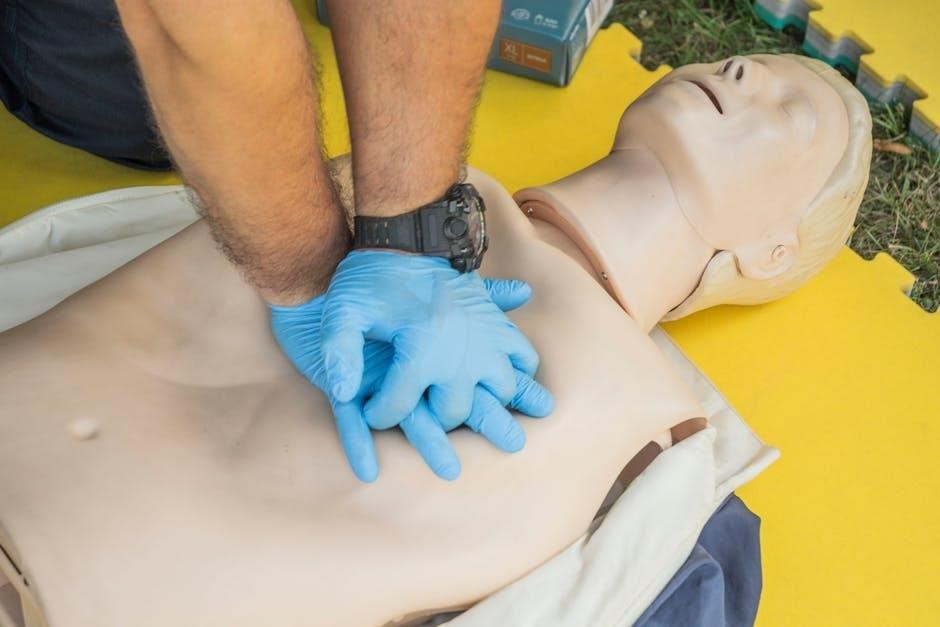
Training and Certification in ILS
ILS training programs offer hands-on sessions and simulations to master life-saving skills․ Certification ensures healthcare professionals are proficient in critical care techniques, enhancing patient outcomes significantly․
4․1 Overview of ILS Training Programs
Immediate Life Support (ILS) training programs are structured to equip healthcare professionals with essential skills to manage critically ill patients effectively․ These programs emphasize a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical training, focusing on patient assessment, airway management, breathing support, and cardiac arrest interventions․ Participants engage in simulation-based learning to practice real-life scenarios, enhancing their decision-making and teamwork abilities․ Experienced instructors guide learners through hands-on sessions, ensuring proficiency in critical care techniques․ The curriculum is designed to align with the content of the Immediate Life Support Manual, making it a valuable resource for preparation and reference․ By completing these programs, healthcare providers gain the confidence and expertise to deliver high-quality care in emergency situations․
4․2 Assessment Methods and Certification Process
The certification process for Immediate Life Support (ILS) involves rigorous assessment methods to ensure competency in critical care skills․ Participants undergo both theoretical and practical evaluations, including scenario-based simulations and objective structured clinical examinations (OSCEs)․ Written tests assess knowledge of protocols and guidelines, while hands-on assessments evaluate proficiency in techniques like airway management and cardiac arrest response․ Successful completion results in certification, recognized by professional bodies․ The process emphasizes adherence to standards outlined in the Immediate Life Support Manual, ensuring providers are well-prepared to deliver effective care․ Continuous learning and recertification are encouraged to maintain expertise and adapt to evolving practices in emergency medicine․

Preventing Complications and Improving Outcomes
Monitoring patients closely and recognizing early warning signs are critical to preventing complications․ Implementing evidence-based interventions and providing post-resuscitation care can significantly improve survival rates and long-term outcomes․
5․1 Monitoring and Early Recognition of Deterioration
Monitoring patients in real-time is essential for detecting subtle changes in their condition․ Regular assessment of vital signs, such as heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure, helps identify potential issues early․ Additionally, monitoring neurological status, including level of consciousness and pupillary reactions, provides critical insights․ Early recognition of deterioration allows for timely interventions, improving patient outcomes․ Healthcare providers should remain vigilant for signs like tachypnea, tachycardia, or decreased oxygen saturation, which may indicate impending compromise․ A systematic approach to patient assessment ensures no abnormalities are missed․ Early intervention can prevent complications and improve survival rates significantly․
5․2 Post-Resuscitation Care and Support
Post-resuscitation care is critical for ensuring patient recovery after cardiac arrest․ It involves supportive measures to stabilize the patient and prevent further complications․ Key aspects include monitoring vital signs, managing oxygen therapy, and maintaining normothermia to prevent neurological damage․ Neurological assessment is essential to determine the extent of brain function recovery․ Additionally, psychological support for both the patient and their family is vital during this phase․ A structured approach to post-resuscitation care improves long-term outcomes and reduces the risk of secondary complications․ Prompt intervention and tailored treatment plans are necessary to address individual patient needs effectively․ This phase requires close collaboration among healthcare teams to optimize recovery and quality of life․

Accessing the Immediate Life Support Manual
The Immediate Life Support Manual is freely available online, ensuring easy access for healthcare professionals․ Download the latest version from official medical training websites or trusted repositories․
6․1 Free Download Options and Resources
The Immediate Life Support (ILS) Manual is widely available for free download from reputable medical education platforms․ Official websites of medical training organizations, such as the Resuscitation Council, provide direct links to the latest versions․ Additionally, professional associations and healthcare institutions often host downloadable copies, ensuring accessibility for all healthcare professionals․ The manual is typically offered in PDF format, making it easy to access on various devices․ Some platforms may require registration or verification of professional status to download․ Ensure authenticity by sourcing from trusted providers to guarantee the most updated and accurate content․ Regularly check for updates to stay informed with the latest guidelines and practices in immediate life support care․
6․2 Additional Materials and Guides
Supplementing the Immediate Life Support (ILS) Manual, various additional materials are available to enhance learning and practical application․ These include training videos, interactive simulations, and downloadable worksheets․ Many websites offering the manual also provide complementary guides, such as quick reference cards and skill sheets․ These resources are designed to reinforce key concepts, like the ABCDE approach and cardiac arrest management․ Some platforms offer mobile apps for on-the-go access to ILS content․ Additionally, webinars and online forums hosted by medical training organizations can provide further insights and updates․ These supplementary materials are invaluable for healthcare professionals seeking to deepen their understanding and improve their proficiency in immediate life support techniques․ Utilizing these resources ensures comprehensive and continuous skill development․

The Immediate Life Support Manual is a vital resource for saving lives, offering free access to critical techniques and guidelines for emergency care professionals worldwide․

7․1 The Role of ILS in Saving Lives
The Immediate Life Support (ILS) manual plays a pivotal role in saving lives by equipping healthcare professionals with essential skills to manage critically ill patients effectively․ Its structured approach ensures timely interventions, improving patient outcomes significantly․ By focusing on early recognition and systematic assessment, ILS empowers responders to act decisively in high-stakes situations․ The manual’s emphasis on evidence-based practices, such as the ABCDE approach, enables healthcare providers to prioritize life-saving actions efficiently․ This comprehensive guide is indispensable for ensuring the best possible care during emergencies, ultimately reducing mortality rates and enhancing the quality of life for patients worldwide․
7․2 Encouraging Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Continuous learning and skill development are essential for mastering Immediate Life Support (ILS) techniques․ The free availability of the ILS manual ensures that healthcare professionals can access updated protocols and guidelines without barriers․ Regular review of the manual fosters a culture of ongoing education, enabling practitioners to refine their skills and stay abreast of the latest advancements in life-saving interventions․ Encouraging hands-on training and recurrent assessments further reinforces competency, ensuring that professionals are prepared to respond effectively in critical situations․ By promoting lifelong learning, the ILS manual empowers healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and saving lives․

